此教程跟随慕课网实战课程进行:https://coding.imooc.com/class/117.html
环境搭建
开发全程使用的ide是idea,数据库使用的是MySQL,开发系统用的是linux centos7.3,前端的技术栈是vue,但是本课程只注重后端部分,前端部分不涉及
安装apache maven
请访问Maven的下载页面:http://maven.apache.org/download.html,其中包含针对不同平台的各种版本的Maven下载文件。
解压apache-maven-3.5.4-bin.zip,并把解压后的文件夹下的apache-maven-3.5.4文件夹移动到C:\Program Files 下。
添加环境变量
右键“计算机”,选择“属性”,之后点击“高级系统设置”,点击“环境变量”,来设置环境变量,有以下系统变量需要配置:
新建系统变量 MAVEN_HOME 变量值:C:\Program Files\apache-maven-3.5.4
编辑系统变量 Path 添加变量值: ;%MAVEN_HOME%\bin
测试安装
在cmd中使用mvn --version命令,成功打印出版本即安装成功
换源
国内访问maven源很慢,因此我们需要将maven源改为阿里镜像,使用mvn -X查找其中的mvn使用的settings文件,我们将默认的settings.xml文件拷贝至用户目录下的.m2文件夹,然后在镜像这一部分中加入:
1 | <mirrors> |
创建项目
通过idea创建项目,选择new->project->Spring Initializr修改好域名和项目名称之后,选择java版本,点击下一步,选择web和mysql/jdbc,如果没有选择jdbc这个内容,就要在pom.xml中配置jdbc
数据库设计
数据库主要包含四个表:
- 商品表
- 类目表
- 订单主表
- 订单详情表
构建数据库的SQL语句如下:
1 | CREATE TABLE `product_info` ( |
然后通过Navicat建立数据库连接,并新建数据库,注意这里的编码要选择utf8mb4,这个编码可以存储诸如emoji表情之类的特殊符号,而传统的utf-8编码则不能
建好之后通过Navicat运行上面的sql脚本,即可生成多个表
日志框架
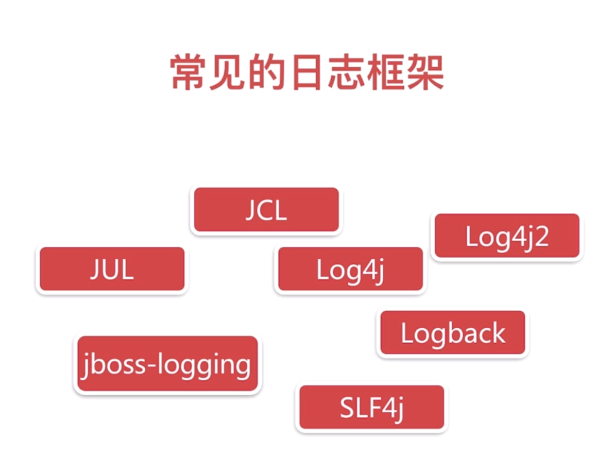
JUL来自官方,但是很多问题,首先淘汰;jboss用得也不多,其次淘汰;log4j和logback是同一个作者,logback是log4j的升级版,logback更好用
log4j2性能很强,但是很多框架不支持,因此删掉
最后我们剩下的就是SLF4j(Simple Logging Facade for Java 简单的java日志外观),Logback
在测试文件夹中新建LoggerTest类
1 | package com.imooc.sell; |
运行测试函数,可以看到info和error这两条信息,但是debug没有看到,这是因为sl4j默认打印info以上的级别的日志,用ctrl+n搜索类,找到sl4j里面的level类,发现有如下五个日志级别:
1 | public enum Level { |
值越大的级别越高
另一种引用SLF4j的方法
在test类上面加入注解@Slf4j,这要求你的idea有Lombok插件,否则下面的log标记无法正常识别,这样就不用定义logger变量
引入Lombok的方法是在pom.xml中添加:
1 | <dependency> |
添加好之后就可以通过下面的方法来引用SLF4j
1 |
|
配置log文件
可以直接通过application.yml配置SLF4j
1 | logging: |
或者是在resources目录下新建一个logback-spring.xml,写入如下配置
1 |
|
买家端开发
首先建立一个dataObject包用于存才各个数据表类
在其中建立ProductCategory类,创建id,名称,编号三个属性,最上面@entity,然后设置好getter和setter方法,在id上面@Id,@GeneratedValue用于表示id和自增
1 | package com.imooc.sell.dataObject; |
当然,如此多的getter和setter方法,可以通过lombok这个包来省去这一步,包括tostring方法也可以省略了,首先在pom.xml中加入dependency
1 | <dependency> |
然后在idea的插件中搜索lombok,安装之后重启idea
在productCategory里面加入一个@Data注解
1 |
|
然后建立一个repository包,用于建立查询,新建ProductCategoryRepository.java,其中的接口继承自JpaRepository,然后后面两个参数是<ProductCategory,Integer>,类名和id类型
1 | package com.imooc.sell.repository; |
现在测试一下ProductCategoryRepository,直接右键点击ProductCategoryRepository,选择goto->test,新建test
1 | package com.imooc.sell.repository; |
点击findoneTest,点击run,此时报错
1 | java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to load ApplicationContext |
这是因为缺少javax.xml.bind.JAXBException包,在pom.xml中引入
1 | <dependency> |
接下来在数据库中手动添加一条数据,就可以实现查询了
因为Spring Boot 2的getOne要求transaction(事务操作),所以要在application.yml中添加no_trans的配置:
1 | Spring: |
接下来实现一下增删改查
1 |
|
这样直接运行会报错,要在项目设置中更改
1 | jpa: |
其中的findByCategoryIdIn方法是定义在ProductCategoryRepository.java中的自定义查找方法,其名字就表明了他的用途,按照规定也只能这样起名字,最后一个in表示sql语句中in的意思
1 | List<ProductCategory> findByCategoryIdIn(List<Integer> categoryTypeList); |
jpa起名规范
Repository接口中声明方法的规范
1、查询方法以 find | read | get 开头;
2、涉及条件查询时,条件的属性用条件关键字连接,要注意的是:条件属性以首字母大写
例如:定义一个 Entity 实体类 class User{
private String firstName;
private String lastName; }
使用And条件连接时,应这样写: findByLastNameAndFirstName(String lastName,String firstName); 条件的属性名称与个数要与参数的位置与个数一一对应
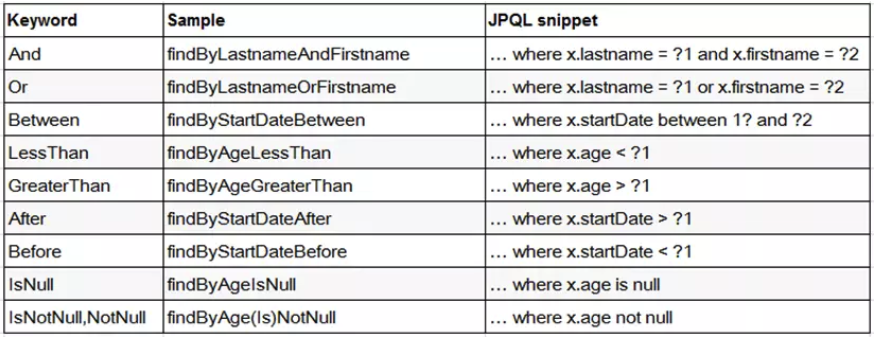
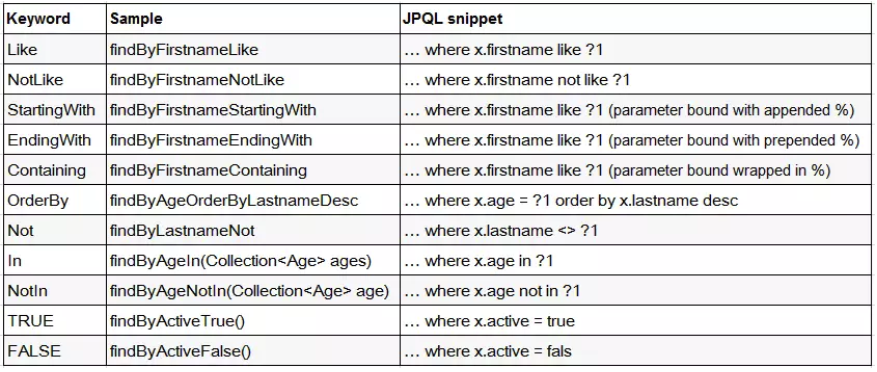
3、直接在接口中定义查询方法,如果是符合规范的,可以不用写实现,目前支持的关键字写法如下:
服务层
新建一个CategoryService.java接口,定义findOne,findAll,findByCategoryIn,save四个方法
1 | public interface CategoryService { |
然后新建impl文件夹,在其中写CategoryServiceImpl.java,用于实现CategoryService接口,记得要@Service
1 |
|
写完这一部分之后开始单元测试
1 |
|
商品相关开发
顺序和之前一样,还是DAO->Service->Controller的顺序
首先我们在dataObject中,定义数据对象entity
1 |
|
然后在repository中定义,与ProductInfo对应的ProductInfoRepository接口
1 | public interface ProductInfoRepository extends JpaRepository<ProductInfo,String> { |
至此DAO相关的定义完成,开始测试相关函数功能
1 |
|
测试全部通过,证明上面开发的部分没有问题
接下来开始写Service层。
DAO和Service层的关系
DAO和Service层的关系
初学Spring的时候,大家可能在DAO和Service层的关系上有些不解,为什么看上去DAO层和Service层做的事情一模一样,如果是这样,那么我们只需要DAO层不就行了吗?这是因为一开始开发的模型比较简单,等到系统越来越复杂的时候,我们查出来的内容可能就不是直接呈现给controller层了,而是经过很多的处理才交给controller层,这个时候的Service层就必不可少了,甚至一些诸如邮件通知之类的功能也可以放在service层,这样可以使controller层变得简洁。
第二个原因是因为用Service层包裹DAO层之后,当有攻击者攻击系统的时候,他只能访问由service层提供的几个函数来访问数据,只能获取少部分数据,而无法对整个数据库进行操作,这从一定程度上保证了数据库的安全性。
在service文件夹中新建ProductService接口,定义如下几个函数
1 |
|
然后再implement实现这个接口
1 |
|
然后新建BuyerProductController.java处理controller层,list这个页面,主要的业务逻辑是:
查出所有上架的商品
查出所有上架商品的categoryType
数据拼装:最外层是code,msg,data
新建一个ResultVO用于存放最外层对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class ResultVO<T> {
//错误码
private Integer code;
//提示信息
private String msg;
//返回的具体内容
private T data;
}新建一个ProductVO用于存放类别
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class ProductVO {
private String CategoryName;
private Integer CategoryType;
private List<ProductInfoVO> productInfoVOList;
}新建一个ProductInfoVO用于存放每个商品的具体信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class ProductInfoVO {
private String productId;
private String productName;
private BigDecimal productPrice;
private String productDescription;
private String productIcon;
}
遍历category,然后再遍历所有product,如果当前的product的categoryType与当前的category相同,通过
BeanUtils.copyProperties拷贝整个对象到另外一个,然后加入到productVOList中,最后设置msg和code,并返回
1 | /** |
发现最后几行有些重复,我们新建一个utils包,用于存放杂件,新建一个ResultVOUtil,新建static方法,以便在上面的return中直接调用return ResultVOUtil.success(productVOList);
1 | public class ResultVOUtil { |
前后端联调
安装node依赖包,运行vue项目
首先cd到文件目录,执行下面的指令安装依赖1
npm install
然后执行
npm run dev,即可运行前端项目刷新前端项目,发现前端的list指向的地址的端口有问题,因此用vscode搜索相关的地址之后可以找到vue项目设置的list函数的地址,并更改为
http://127.0.0.1:8080/sell/buyer/product/list更改之后重新运行项目,发现可以访问了,但是没有数据返回,此时只需要在list函数上加入一个跨域访问的注解
@CrossOrigin("*"),即可正常访问。
订单层开发
同样开发顺序是DAO->Service->Controller,具体一点,先是定义dataObject,然后定义repository,这两部分组成了DAO层
订单DAO层开发
dataObject定义
订单一共有两个表,一个是OrderDetail(详情表),一个是OrderMaster(主表),对照数据库,定义每一个字段
- 首先定义OrderMaster表,
@DynamicUpdate用于动态更新updateTime,
1 |
|
- 定义OrderDetail表
1 |
|
其中用到的状态表示,要用枚举来表示,不至于那么乱
首先是OrderStatusEnum列举订单状态
1 |
|
然后是PayStatusEnum枚举支付状态
1 |
|
repository定义及测试
对应两个dataObject,定义两个repository
OrderMasterRepository用于操作OrderMaster表
1 | public interface OrderMasterRepository extends JpaRepository<OrderMaster,String> { |
OrderDetailRepository用于操作OrderDetail表
1 | public interface OrderDetailRepository extends JpaRepository<OrderDetail,String> { |
至此,两个repository完成,开始测试
OrderMasterRepositoryTest用于测试OrderMasterRepository
1 |
|
OrderDetailRepositoryTest用于测试OrderDetailRepository
1 |
|
至此,订单DAO层开发完成,接下来开发Service层
订单Service层开发
创建一个名为OrderService.java的接口,包含以下6个方法
1 | public interface OrderService { |
创建ProductServiceImpl.java实现上面的接口
其中需要用到一个Data Transform Object,名称为OrderDTO,其大部分字段与OrderMaster一样,多了一个List<OrderDetail> orderDetailList字段,用于保存每个订单对应的OrderDetail信息,定义如下
1 | //OrderDTO.java |
其中需要用到的SellException定义如下:
1 | public class SellException extends RuntimeException { |
SellException引用的ResultEnum枚举,如下所示:
1 |
|
创建订单
create方法:传入一个orderDTO,查找商品,计算总价
传入的参数如下所示:
1 | name: "张三" |
因此,要通过productId来查询productInfo,然后获取价格乘以数量,得到总价,然后设置DTO的详细信息,设置OrderId和orderDetailId
设置ID的方法写在utils文件夹中,为了不重复,所以加上同步锁
1 | //utils/KeyUtil.java |
第三步是写入OrderMaster,拷贝OrderDTO到OrderMater对象中,设置总价,保存
第四步是扣库存,扣库存的函数是productService.decreaseStock,其中用到的数据转移对象是CartDTO,包含id和数量,定义如下:
1 |
|
扣库存的函数如下,通过id查出商品的库存,减去购物车里面的库存,保存商品信息:
1 |
|
至此,创建订单的开发结束,具体实现如下:
1 |
|
通过订单id查询订单
查询订单相对容易,通过一个id查找到订单主表orderMaster信息,通过id查到所有订单详情表的orderDetail信息,返回一个orderDTO对象
1 |
|
####通过用户id查询订单列表
通过用户的openid来查询订单,要求返回一个page对象,包含的是OrderDTO类型
1 |
|
其中的findByBuyerOpenid方法定义如下
1 | //repository/OrderMasterRepository.java |
取消订单
首先判断订单是不是新下单状态,不是则抛出异常
如果是新下单,修改订单为取消状态
返还库存:
增加库存的函数如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public void increaseStock(List<CartDTO> cartDTOList) {
for (CartDTO cartDTO : cartDTOList) {
ProductInfo productInfo = repository.findById(cartDTO.getProductId()).orElse(null);
if (productInfo == null) {
throw new SellException(ResultEnum.PRODUCT_NOT_EXIST);
}
Integer result = productInfo.getProductStock() + cartDTO.getProductQuantity();
productInfo.setProductStock(result);
repository.save(productInfo);
}
}如果已支付,退款:因为现在支付相关的函数还没有完成,因此这部分先空着,用
//TODO来表示,这样点击左下角的TODO按钮,即可快速浏览这部分内容
1 |
|
完结订单
与取消订单相似,首先判断订单状态,如果是新下单,可以修改为完结并保存,
1 |
|
退款
首先判断订单状态,然后判断支付状态,最后修改支付状态
1 |
|
订单Service测试
测试代码如下:
1 |
|
订单Controller层开发
开发一个create页面,参数是一个OrderForm,其定义如下
1 |
|
要求验证这个form的内容不为空,在定义时加入注解@NotEmpty,参数之前加入注解@Valid
过程中要求把OrderFrom转换为OrderDTO,在converter包中新建类OrderForm2OrderDTO,用google的Gson工具,将string转换为对象,在pom.xml中需要加入依赖:
1 | <dependency> |
OrderForm2OrderDTO定义如下:
1 |
|
查找订单的内容,需要判断用户id和订单是不是一样,我们将这部分代码放在BuyerService当中:
1 |
|
controller的定义如下:
1 |
|
后面的内容主要是关于支付的,等开发有需要的时候再研究这部分。